NICS Analyses with NICSgen
NICSgen is end of support. The basic functionalities have been combined into py.Aroma, a multi-functional tool for aromaticity analyses. Please check the homepage of py.Aroma for more information.
Contents
1. Statement of need
NICS (Nucleus-Independent Chemical Shifts) is a popular method for analyzing aromaticity of cyclic compound, by calculating the magnetic shielding tensor (in ppm) with NMR calculation. In NICS calculation, ghost atoms (Bq) are needed to be included in the input file. NICS(n) is widely used for n = 0 and n = 1 (Which NICS aromaticity index for planar π rings is best?), we need to add the ghost atom to the height of 1 Å from the center point of the plane. It is difficult to add the ghost atom accurately. So, I present the Python program NICSgen, to help user add the ghost atom in the right position.
NICSgen could be download from homepage and GitHub. To install and run the programs, please refer to the user manuals
2. Mathematic Principle
Imagine we have m (m >= 3) points p on plane in Cartesian coordinate space system, the coordinates of these points are:
\[p_1 = (x_1,y_1,z_1)\] \[p_2 = (x_2,y_2,z_2)\] \[p_3 = (x_3,y_3,z_3)\] \[\cdots\] \[p_m = (x_m,y_m,z_m)\]So, the center point p(c) of these point should be located at:
\[p_c = (x_c,y_c,z_c),{\rm where:}\] \[x_c=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m x_i,\:y_c=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m y_i,\:z_c=\frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^m z_i\]The coordinates of p(c) is the ghost atom for NICS(0) calculation.
Next, for NICS(n): we need to add the ghost atom to the height of n Å from the center point of the plane. Here is the common solution:
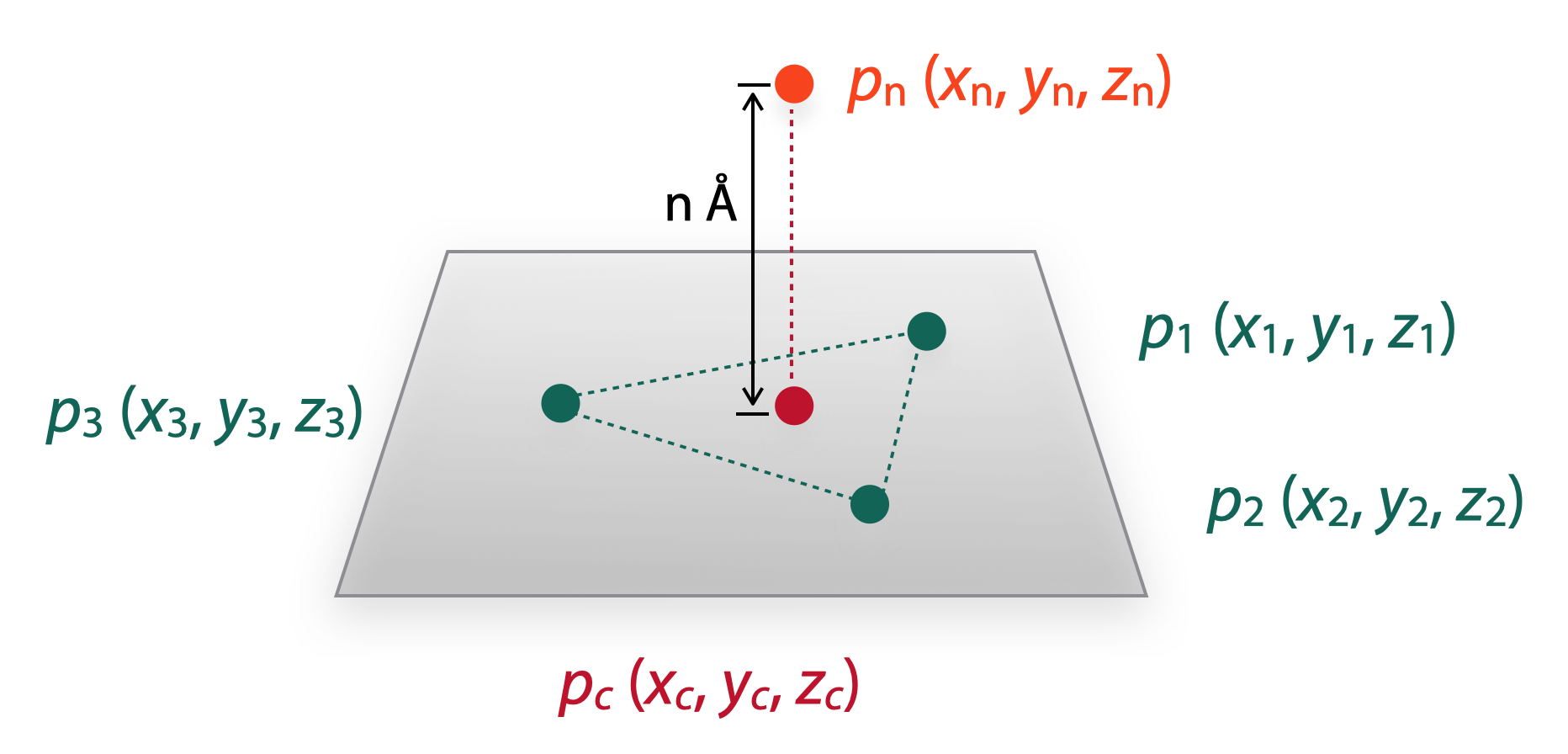
Vector n is the normal vector of plane Π, so,
\[\because \overrightarrow{n} \bot \Pi\] \[\therefore \overrightarrow{n}=\overrightarrow{p_1p_2} \times \overrightarrow{p_1p_3} = \begin{vmatrix} i & j & k \\ x_2-x_1 & y_2-y_1 & z_2-z_1 \\ x_3-x_1 & y_3-y_1 & z_3-z_1 \end{vmatrix} = a \overrightarrow{i} + b \overrightarrow{j} + c \overrightarrow{k} =(a,b,c)\]thus,
\[a=(y_2-y_1)(z_3-z_1)-(y_3-y_1)(z_2-z_1)\] \[b=(z_2-z_1)(x_3-x_1)-(z_3-z_1)(x_2-x_1)\] \[c=(x_2-x_1)(y_3-y_1)-(x_3-x_1)(y_2-y_1)\]The vector p(c)p(n) should be parallel with normal vector, so:
\[\because \overrightarrow{p_n p_c} \parallel \overrightarrow{n}\] \[\therefore \overrightarrow{p_n p_c} = (x_n-x_c,y_n-y_c,z_n-z_c)=\lambda \overrightarrow{n}\]thus,
\[\frac {\overrightarrow{p_n p_c}}{\overrightarrow{n}} = \frac {x_n-x_c}{a} = \frac {y_n-y_c}{b} = \frac {z_n-z_c}{c} =\lambda\]therefore, we can solve the equation to get the values of x(n), y(n) and z(n).
3. NICS analyses of 1-methylazulene
Calculation files in this section could be download from here. 1-Methylazulene was optimized at ωB97X-D/6-31G(d) level of theory with Gaussian 16 B.01 package. The optimized azulene is located on XY plane (Figure1). I want to know the NICS(0) values of 7- and 5-membered rings, and the NICS(1) of 7-membered ring.
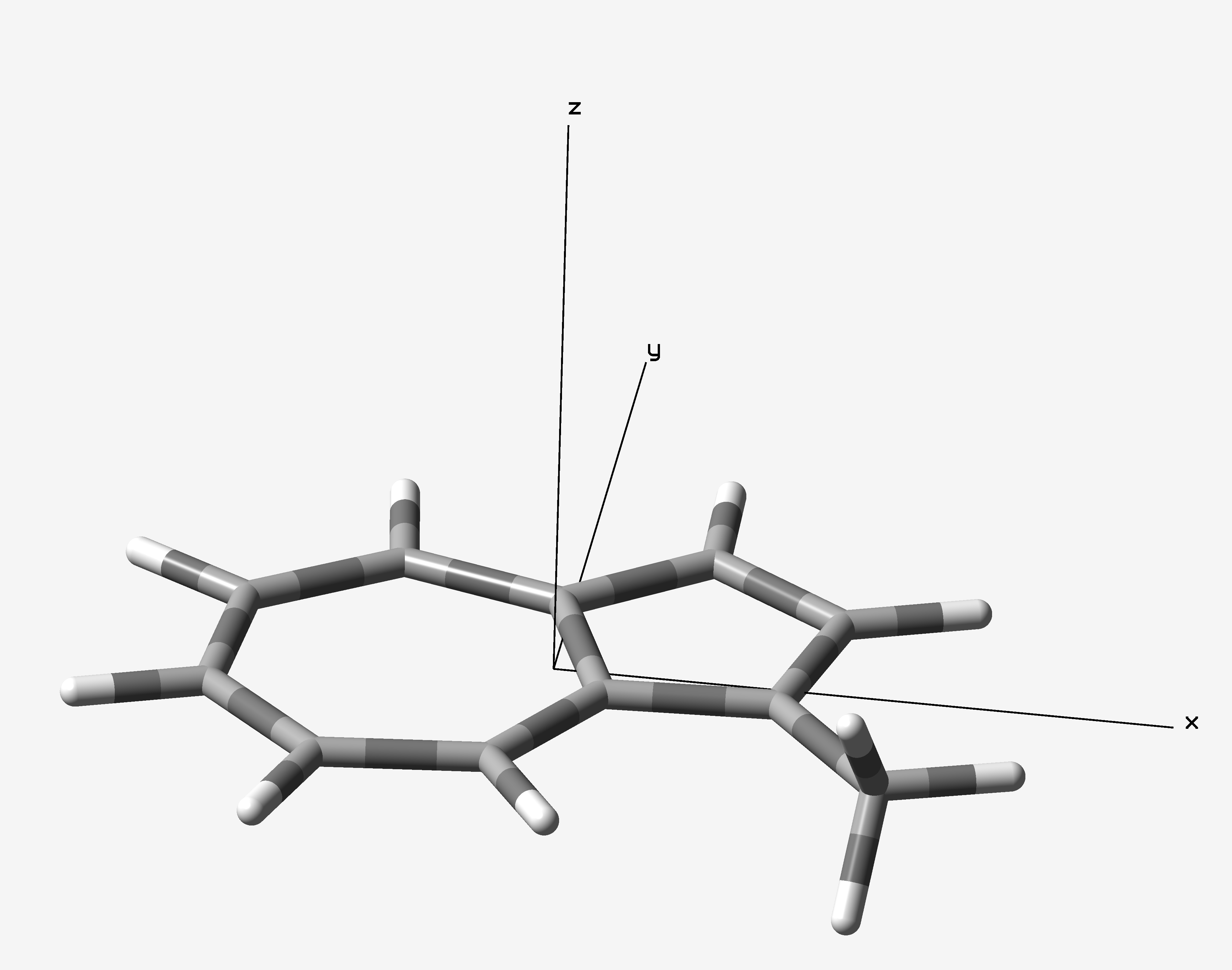
Figure 1. Optimized geometry of 1-methylazulene.
The input file for NICS calculation was created by NICSgen, the input geometry is shown in Figure 2. For NICS calculation, B3LYP/6-31G+(d) or higher level of theory is recommended.
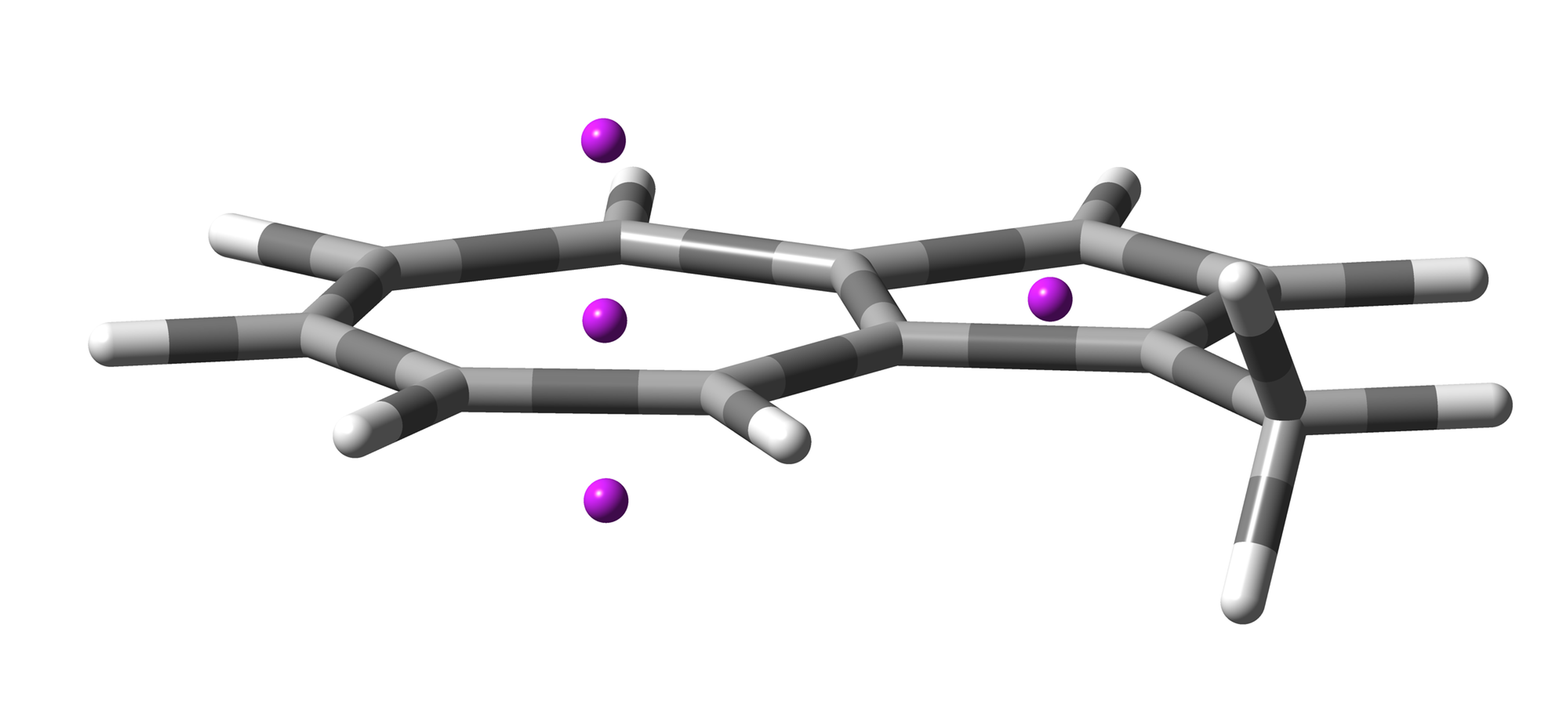
Figure 2. Input geometry for NICS calculation.
We can find the magnetic shielding tensors of these ghost atoms in the output file, and the NICS values are the reversed magnetic shielding tensors:
NICS(0)zz = -7.6656 (7-membered ring)
NICS(0)zz = -30.1781 (5-membered ring)
NICS(1)zz = -19.8181
NICS(-1)zz = -19.8172
This results are in accordance with the 2D-ICSS and 3D-ICSS analyses.
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: